How to setup Teleport to securely access your servers

This tutorial will explain why you should use Teleport instead of SSH to manage your servers and how to install it.
What is Teleport
Gravitational Teleport is a gateway for managing access to clusters of Linux servers via SSH or the Kubernetes API. It is intended to be used instead of traditional OpenSSH for organizations that need to:
- Secure their infrastructure and comply with security best-practices and regulatory requirements.
- Have complete visibility into activity happening across their infrastructure.
- Reduce the operational overhead of privileged access management across both traditional and cloud-native infrastructure.
Teleport aims to be a cloud-native SSH solution, i.e. it makes it natural to think of environments, not servers. Below is a list of the most popular Teleport features:
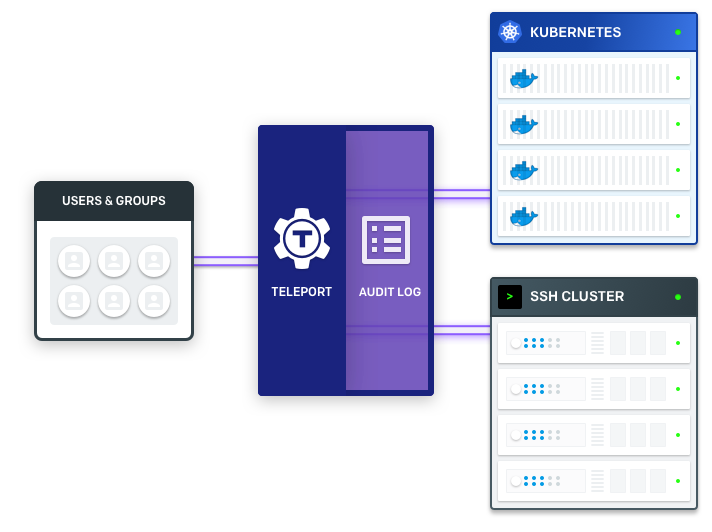
- Single SSH/Kubernetes access gateway for an entire organization.
- SSH certificate based authentication instead of static keys.
- Avoid key distribution and trust on first use issues by using auto-expiring keys signed by a cluster certificate authority (CA).
- Enforce 2nd factor authentication.
- Connect to clusters located behind firewalls without direct Internet access via SSH bastions.
- Collaboratively troubleshoot issues through session sharing.
- Discover online servers and Docker containers within a cluster with dynamic node labels.
- The ability to manage trust between teams, organizations and data centers.
- SSH/Kubernetes access into behind-firewall environments without any open ports.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) for SSH.
- A single tool (“pane of glass”) to manage RBAC for both SSH and Kubernetes.
- Audit log with session recording/replay.
- Kubernetes audit log, including the recording of interactive commands executed via
kubectl. - The same workflows and ease of use that devs get with familiar
ssh/kubectlcommands. - Ability to run in “agentless” mode, i.e. most Teleport features are available on clusters with pre-existing SSH daemons, usually
sshd.
Why use Teleport
Definitions
| CONCEPT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Node | Synonym to “server” or “computer”, something one can “SSH to”. A node must be running the teleport daemon with “node” role/service turned on. |
| Certificate Authority (CA) | A pair of public/private keys Teleport uses to manage access. A CA can sign a public key of a user or node, establishing their cluster membership. |
| Teleport Cluster | A Teleport Auth Service contains two CAs. One is used to sign user keys and the other signs node keys. A collection of nodes connected to the same CA is called a “cluster”. |
| Cluster Name | Every Teleport cluster must have a name. If a name is not supplied via teleport.yaml configuration file, a GUID will be generated. IMPORTANT: renaming a cluster invalidates its keys and all certificates it had created. |
| Trusted Cluster | Teleport Auth Service can allow 3rd party users or nodes to connect if their public keys are signed by a trusted CA. A “trusted cluster” is a pair of public keys of the trusted CA. It can be configured via teleport.yaml file. |
Get the software
To install, download the official binaries from the Teleport Downloads section and run:
$ tar -xzf teleport-v4.2.8-linux-amd64-bin.tar.gz
$ sudo ./install
This will install teleport but will not run it
Get SSL cert from Let’s Encrypt
This is used to secure the website connection.
Add Certbot PPA
You’ll need to add the Certbot PPA to your list of repositories. To do so, run the following commands on the command line on the machine:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
sudo apt-get update
Install Certbot
Run this command on the command line on the machine to install Certbot.
sudo apt-get install certbot
Run certbot
Make sure the port 80 is not being used by any other application and then run
sudo certbot certonly --standalone
and answer the prompts that follow
The certs will be stored in /etc/letsencrypt/live/ directory
Test automatic renewal
The Certbot packages on your system come with a cron job or systemd timer that will renew your certificates automatically before they expire. You will not need to run Certbot again, unless you change your configuration. You can test automatic renewal for your certificates by running this command:
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Create teteport data directory
Teleport stores data in /var/lib/teleport. Make sure that regular/non-admin users do not have access to this folder on the Auth server.
sudo mkdir /var/lib/teleport
systemd unit file
Create the systemd unit file to start the teleport daemon via the init system. This file should be saved at /etc/systemd/system/teleport.service
[Unit]
Description=Teleport SSH Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/teleport start --config=/etc/teleport.yaml --pid-file=/var/run/teleport.pid
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
PIDFile=/run/teleport.pid
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Configure teleport
teleport can be run using default setting usign teleport start. This is useful for demo or testing but not for production. For production configure etc\teleport.yaml properly.
For this you can use get the default settings file from teleport by running teleport configure which dumps a sample configuration file in YAML format into standard output. Take this output and make changes as required.
Our teleport configuration
Sample configuration is located at https://gist.github.com/vairisingh/ed9028a2403bb2b328cc2ceee8becbf8
Enable ufw
sudo ufw status
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow http
sudo ufw allow 3022
sudo ufw allow 3023
sudo ufw allow 3024
sudo ufw allow 3025
sudo ufw allow 3026
sudo ufw allow 3080
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw status verbose
Start teleport
Use the following commands to start teleport
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable teleport
sudo systemctl start teleport
# check whether teleport is running
sudo systemctl status
sudo systemctl status teleport
journalctl -fu teleport
- Indivar Software Solutions Pvt Limited, India and New Zealand: Co-Founder and CTO
- Credence Medicure Corporation: Co-Founder & Director - IT
- Stakteck Limited: Co-Founder and CTO